Uncertainty analysis#
Uncertainty analysis of the critical head difference#
In this example, we demonstrate how to perform an uncertainty analysis of a model. The goal of such an analysis is to estimate the uncertainty in the model output resulting from uncertain input parameters.
We focus on the critical head difference model according to Sellmeijer. This model is applicable to the piping failure mechanism, which describes backward internal erosion beneath dikes with horizontal seepage paths.
Define model#
First, let’s import the necessary packages:
[25]:
from probabilistic_library import UncertaintyProject, DistributionType, UncertaintyMethod
The critical head difference, \(H_c\), according to the Sellmeijer’s model is described by the following equations:
\(F_{resistance}=\eta\cdot \frac{\gamma_{sub,particles}}{\gamma_{water}}\cdot \tan \theta_{sellmeijer,rev}\)
\(F_{scale}=\frac{d_{70.m}}{\sqrt[3]{\kappa\cdot L}}\cdot\left(\frac{d_{70}}{d_{70.m}}\right)^{0.4}\) and \(\kappa = \frac{\nu_{water}}{g}\cdot k\)
\(F_{geometry}=0.91\cdot \left(\frac{D}{L}\right)^{\frac{0.28}{\left(\frac{D}{L}\right)^{2.8}-1}+0.04}\)
\(H_c = F_{resistance} \cdot F_{scale} \cdot F_{geometry} \cdot L\)
where: \(L\) - seepage length (m) \(D\) - thickness of upper sand layer (m) \(\theta\) - bedding angle (\(\circ\)) \(d_{70}\) - particle diameter (m) \(k\) - permeability of the upper sand layer (m/s)
[26]:
from utils.models import model_sellmeijer
label_critical_head_diff = "critical head difference (m)"
label_pdf = "pdf (-)"
Uncertainty analysis#
We begin by creating an uncertainty project and defining the model:
[27]:
project = UncertaintyProject()
project.model = model_sellmeijer
project.model.print()
Model model_sellmeijer:
Input parameters:
k
L
d70
D
Output parameters:
delta_h_c
We define all the input parameters of the model as random variables:
[28]:
project.variables["k"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["k"].mean = 0.000245598
project.variables["k"].variation = 0.25
project.variables["L"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["L"].mean = 40.0
project.variables["L"].variation = 0.25
project.variables["d70"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["d70"].mean = 0.00019
project.variables["d70"].variation = 0.25
project.variables["D"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["D"].mean = 30.0
project.variables["D"].variation = 0.25
Uncertainty analysis can be performed using one of the following methods: crude_monte_carlo, numerical_integration, fosm, form, importance_sampling or directional_sampling.
The results can be accessed from project.stochast.
Crude Monte Carlo#
Let’s consider the crude_monte_carlo method:
[29]:
project.settings.uncertainty_method = UncertaintyMethod.crude_monte_carlo
project.settings.minimum_samples = 4000
project.settings.maximum_samples = 5000
project.run()
uncer = project.stochast
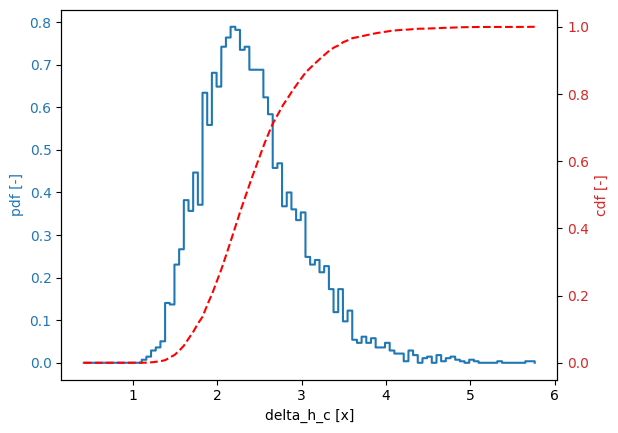
uncer.print()
uncer.plot()
Variable delta_h_c:
distribution = histogram
Definition:
amount[1.101, 1.157] = 2
amount[1.157, 1.212] = 4
amount[1.212, 1.268] = 8
amount[1.268, 1.323] = 10
amount[1.323, 1.379] = 14
amount[1.379, 1.434] = 39
amount[1.434, 1.49] = 38
amount[1.49, 1.545] = 64
amount[1.545, 1.601] = 74
amount[1.601, 1.656] = 106
amount[1.656, 1.712] = 99
amount[1.712, 1.767] = 124
amount[1.767, 1.822] = 103
amount[1.822, 1.878] = 176
amount[1.878, 1.933] = 155
amount[1.933, 1.989] = 189
amount[1.989, 2.044] = 180
amount[2.044, 2.1] = 206
amount[2.1, 2.155] = 212
amount[2.155, 2.211] = 219
amount[2.211, 2.266] = 217
amount[2.266, 2.322] = 204
amount[2.322, 2.377] = 206
amount[2.377, 2.433] = 191
amount[2.433, 2.488] = 191
amount[2.488, 2.544] = 191
amount[2.544, 2.599] = 173
amount[2.599, 2.655] = 162
amount[2.655, 2.71] = 127
amount[2.71, 2.766] = 130
amount[2.766, 2.821] = 102
amount[2.821, 2.877] = 111
amount[2.877, 2.932] = 100
amount[2.932, 2.988] = 93
amount[2.988, 3.043] = 98
amount[3.043, 3.099] = 69
amount[3.099, 3.154] = 64
amount[3.154, 3.21] = 67
amount[3.21, 3.265] = 59
amount[3.265, 3.321] = 63
amount[3.321, 3.376] = 48
amount[3.376, 3.432] = 33
amount[3.432, 3.487] = 48
amount[3.487, 3.543] = 27
amount[3.543, 3.598] = 34
amount[3.598, 3.654] = 15
amount[3.654, 3.709] = 13
amount[3.709, 3.765] = 17
amount[3.765, 3.82] = 13
amount[3.82, 3.876] = 16
amount[3.876, 3.931] = 10
amount[3.931, 3.987] = 10
amount[3.987, 4.042] = 13
amount[4.042, 4.098] = 8
amount[4.098, 4.153] = 6
amount[4.153, 4.209] = 6
amount[4.209, 4.264] = 1
amount[4.264, 4.32] = 8
amount[4.32, 4.375] = 5
amount[4.431, 4.486] = 3
amount[4.486, 4.542] = 4
amount[4.597, 4.653] = 5
amount[4.653, 4.708] = 1
amount[4.708, 4.764] = 3
amount[4.764, 4.819] = 4
amount[4.819, 4.875] = 2
amount[4.875, 4.93] = 1
amount[4.986, 5.041] = 2
amount[5.041, 5.097] = 1
amount[5.319, 5.374] = 1
amount[5.652, 5.707] = 1
amount[5.707, 5.763] = 1
Derived values:
mean = 2.414
deviation = 0.5846
variation = 0.2422
Variable definition is not valid, plot can not be made.
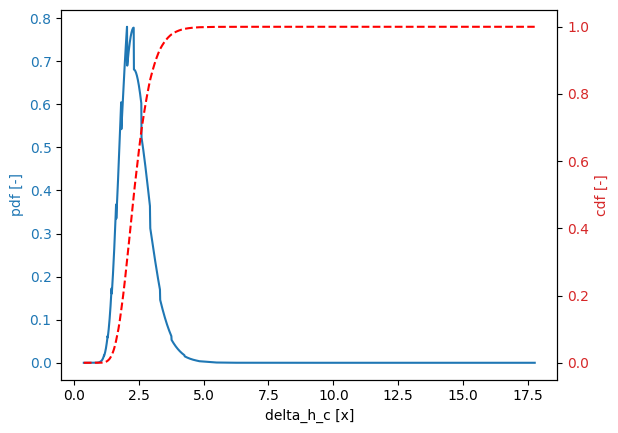
FORM#
The following code demonstrates the uncertainty analysis using form:
[30]:
project.settings.uncertainty_method = UncertaintyMethod.form
project.settings.maximum_iterations = 50
project.run()
uncer = project.stochast
uncer.print()
uncer.plot()
Variable delta_h_c:
distribution = cdf_curve
Definition:
beta[0.413] = -7.985
beta[0.4571] = -7.487
beta[0.5062] = -6.988
beta[0.5607] = -6.49
beta[0.6214] = -5.992
beta[0.6891] = -5.493
beta[0.7647] = -4.995
beta[0.8492] = -4.496
beta[0.9439] = -3.997
beta[1.05] = -3.498
beta[1.17] = -2.999
beta[1.305] = -2.499
beta[1.458] = -2
beta[1.632] = -1.5
beta[1.829] = -1
beta[2.054] = -0.5
beta[2.31] = 0
beta[2.603] = 0.5
beta[2.938] = 1
beta[3.322] = 1.5
beta[3.761] = 2
beta[4.264] = 2.5
beta[4.84] = 2.999
beta[5.499] = 3.499
beta[6.253] = 3.999
beta[7.115] = 4.498
beta[8.1] = 4.998
beta[9.226] = 5.498
beta[10.51] = 5.997
beta[11.98] = 6.497
beta[13.66] = 6.997
beta[15.57] = 7.497
beta[17.76] = 7.996
Derived values:
mean = 2.388
deviation = 0.5795
variation = 0.2427