Gradient methods (FORM, Cobyla)#
Estimation of failure probability due to wave overtopping#
In this example, we will demonstrate the application of the gradient-based reliability methods (form and cobyla_reliability) to estimate the probability of failure of a levee due to wave overtopping.
Define model#
First, we import the necessary classes:
[7]:
from probabilistic_library import ReliabilityProject, DistributionType, ReliabilityMethod
We consider the following limit state function:
\(Z = q_{crit} - q_{o}\)
where:
\(q_{crit}\) is the critical overtopping discharge (m3/s/m)
\(q_{o}\) is the occuring wave overtopping discharge (m3/s/m)
The wave overtopping discharche \(q_{o}\) is derived in this example using simplified equations from [Technical Report Wave Run-up and Wave Overtopping at Dikes, Technical Advisory Committee on Flood Defence, The Netherlands, Delft, May 2002.]. The wave overtopping depends on:
local water level \(h\) (m)
significant wave height \(H_{m0}\) (m)
spectral wave period \(T_{m-1,0}\) (s)
wave direction with respect to North
dike normal with respect to North
crest height \(y_{crest}\) (m)
[8]:
from utils.models import z_func_overtopping
To perform a reliability analysis, we create a reliability project and specify the limit state function (model):
[9]:
project = ReliabilityProject()
project.model = z_func_overtopping
project.model.print()
Model z_func_overtopping:
Input parameters:
h
hm0
tm10
wave_direction
dike_normal
y_crest
q_crit
Output parameters:
Z
We assume the following distributions for the parameters present in the limit state function:
[10]:
project.variables["h"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["h"].mean = 1.5
project.variables["h"].deviation = 0.05
project.variables["hm0"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["hm0"].mean = 1.5
project.variables["hm0"].deviation = 0.25
project.variables["tm10"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["tm10"].mean = 3
project.variables["tm10"].deviation = 0.5
project.variables["wave_direction"].distribution = DistributionType.deterministic
project.variables["wave_direction"].mean = 0.0
project.variables["dike_normal"].distribution = DistributionType.deterministic
project.variables["dike_normal"].mean = 0.0
project.variables["y_crest"].distribution = DistributionType.deterministic
project.variables["y_crest"].mean = 6.0
project.variables["q_crit"].distribution = DistributionType.log_normal
project.variables["q_crit"].mean = 0.001
project.variables["q_crit"].deviation = 0.01
Perform reliability calculations with FORM#
We start with the reliability method form. The reliability analysis is executed using project.run(), and the results are accessed from project.design_point.
[ ]:
project.settings.reliability_method = ReliabilityMethod.form
project.settings.relaxation_factor = 0.75
project.settings.maximum_iterations = 150
project.settings.epsilon_beta = 0.01
project.settings.save_realizations = True
project.settings.save_convergence = True
project.run()
project.design_point.print()
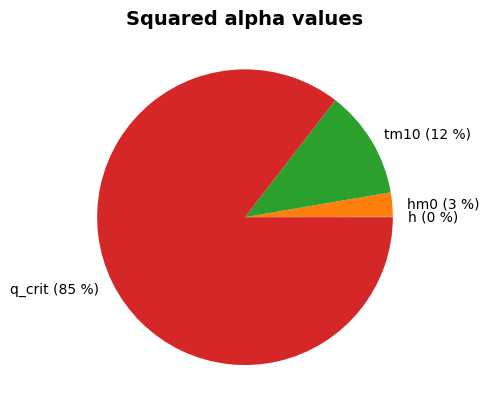
project.design_point.plot_alphas()
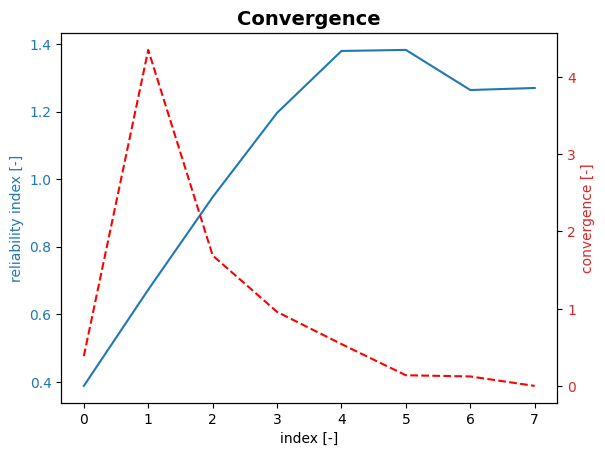
project.design_point.plot_convergence()
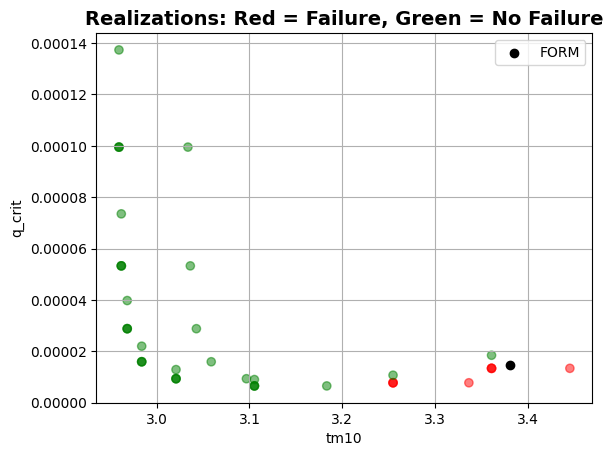
project.design_point.plot_realizations()
Reliability (FORM)
Reliability index = 1.27
Probability of failure = 0.1021
Convergence = 0.002751 (converged)
Model runs = 40
Alpha values:
h: alpha = -0.03435, x = 1.501
hm0: alpha = -0.3222, x = 1.583
tm10: alpha = -0.6338, x = 3.381
wave_direction: alpha = 0, x = 0
dike_normal: alpha = 0, x = 0
y_crest: alpha = 0, x = 6
q_crit: alpha = 0.7024, x = 1.465e-05
Perform reliability calculations with Cobyla algorithm#
We now conduct the reliability analysis using the cobyla_reliability method.
[13]:
project.settings.reliability_method = ReliabilityMethod.cobyla_reliability
project.settings.maximum_iterations = 200
project.settings.epsilon_beta = 0.01
project.run()
project.design_point.print()
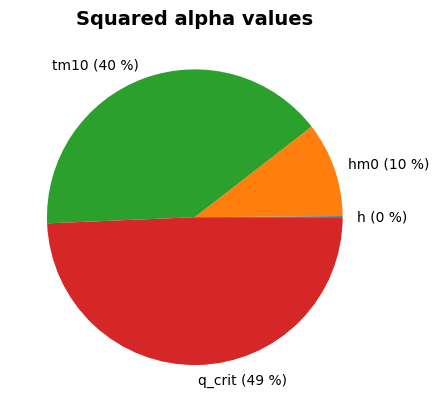
project.design_point.plot_alphas()
Reliability (Cobyla Reliability)
Reliability index = 1.315
Probability of failure = 0.09434
Model runs = 201
Alpha values:
h: alpha = 0.02234, x = 1.498
hm0: alpha = -0.1624, x = 1.533
tm10: alpha = -0.3441, x = 3.189
wave_direction: alpha = 0, x = 0
dike_normal: alpha = 0, x = 0
y_crest: alpha = 0, x = 6
q_crit: alpha = 0.9245, x = 7.312e-06