Update a Wflow model: forcing#
Once you have a Wflow model, you may want to update your model in order to use a new landuse map, change a parameter value, add sample locations, use different forcing data, create and run different scenarios etc.
With HydroMT, you can easily read your model and update one or several components of your model using the update function of the command line interface (CLI). Here are the steps and some examples on how to update the model forcing.
All lines in this notebook which starts with ! are executed from the command line. Within the notebook environment the logging messages are shown after completion. You can also copy these lines and paste them in your shell to get more feedback.
Import packages#
In this notebook, we will use some functions of HydroMT to plot the precipitation from the original and updated models. Here are the libraries to import to realize these steps.
[1]:
import xarray as xr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Model setup configuration#
Updating landuse is an easy step with the command line but sometimes, for example with forcing, you want to update several things at the same time. This is possible by preparing a configuration file that includes every methods and settings that you want to do during your update.
The HydroMT configuration file (YAML) contains the model setup configuration and determines which methods are updated and in which sequence and sets optional arguments for each method. This configuration is passed to hydromt using -i <path_to_config_file>.
Each header (without indent) (e.g. setup_precip_forcing:) corresponds with a model method which are explained in the docs (model methods).
Let’s open the example configuration file wflow_update_forcing.yml from the model repository [examples folder] and have a look at the settings.
[2]:
fn_config = "wflow_update_forcing.yml"
with open(fn_config, "r") as f:
txt = f.read()
print(txt)
steps:
- setup_config: # options parsed to wflow toml file <section>.<option>
data:
time.starttime: 2010-02-01T00:00:00
time.endtime: 2010-02-10T00:00:00
time.timestepsecs: 86400
input.path_forcing: inmaps-chirps.nc
- setup_precip_forcing:
precip_fn: chirps_global # source for precipitation.
- setup_temp_pet_forcing:
temp_pet_fn: era5 # source for temperature and potential evapotranspiration.
press_correction: True # if True temperature is corrected with elevation lapse rate.
temp_correction: True # if True pressure is corrected with elevation lapse rate.
dem_forcing_fn: era5_orography # source of elevation grid corresponding to temp_pet_fn. Used for lapse rate correction.
pet_method: debruin # method to compute PET: {debruin, makkink}
skip_pet: False # if True, only temperature is prepared.
- forcing.write: # Write forcing and re-write config if forcing filename or times are updated
output_frequency: M # Set frequency at which forcing files are written, following pandas offset aliases
- staticmaps.write: # to make sure that the staticmaps are written as well, can be skipped if update in the same model folder
- geoms.write: # to make sure that the staticgeoms are written as well, can be skipped if update in the same model folder
- config.write: # to make sure the configurations file is written with the updated start and endtime and the forcing file path
Here we can see that to fully update wflow forcing, we will run three methods of Wflow:
setup_config: modifies the Wflow TOML configuration file and tells hydroMT what are the start, end, timestep of the forcing data we want to prepare. Note that you can change any options in the TOML file here, including for example the name of the output forcing file with the option input.path_forcing.
setup_precip_forcing: tells hydroMT how to prepare precipitation data including from which data source and with or without downscaling.
setup_temp_pet_forcing: tells hydroMT how to prepare temperature and potential evapotranspiration data including which data source, which computation method for PET and with or without downscaling.
We also decide to not write our forcing not as one file but one file per month.
You can find more information on the different methods and their options in the docs (model methods).
Here we can see that we will prepare daily forcing for 10 days in February 2010 using CHIRPS for precipitation and ERA5 for temperature and potential evapotranspiration.
HydroMT CLI update interface#
Using the HydroMT build API, we can update one or several components of an already existing Wflow model. Let’s get an overview of the available options:
[3]:
# Print the options available from the update command
! hydromt update --help
Usage: hydromt update [OPTIONS] MODEL MODEL_ROOT
Update a specific component of a model.
Set an output directory to copy the edited model to a new folder, otherwise
maps are overwritten.
Example usage: --------------
Update Wflow model components outlined in an .yml configuration file and
write the model to a directory: hydromt update wflow_sbm /path/to/model_root
-o /path/to/model_out -i /path/to/wflow_config.yml -d
/path/to/data_catalog.yml -v
Options:
-o, --model-out DIRECTORY Output model folder. Maps in MODEL_ROOT are
overwritten if left empty.
-i, --config PATH Path to hydroMT configuration file, for the model
specific implementation. [required]
-d, --data TEXT Path to local yaml data catalog file OR name of
predefined data catalog.
--dd, --deltares-data Flag: Shortcut to add the "deltares_data" catalog
--fo, --force-overwrite Flag: If provided overwrite existing model files
--cache Flag: If provided cache tiled rasterdatasets
-q, --quiet Decrease verbosity.
-v, --verbose Increase verbosity.
--help Show this message and exit.
Update Wflow forcing layers#
[4]:
# NOTE: copy this line (without !) to your shell for more direct feedback
! hydromt update wflow_sbm wflow_piave_subbasin -o ./wflow_piave_forcing -i wflow_update_forcing.yml -d artifact_data -v
2026-01-14 11:21:20,419 - hydromt - log - INFO - HydroMT version: 1.3.0
2026-01-14 11:21:20,550 - hydromt.data_catalog.data_catalog - data_catalog - INFO - Reading data catalog artifact_data latest
2026-01-14 11:21:20,550 - hydromt.data_catalog.data_catalog - data_catalog - INFO - Parsing data catalog from /home/runner/.hydromt/artifact_data/v1.0.0/data_catalog.yml
2026-01-14 11:21:21,190 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - Initializing wflow_sbm model from hydromt_wflow (v1.0.1.dev0).
2026-01-14 11:21:21,190 - hydromt.data_catalog.data_catalog - data_catalog - INFO - Parsing data catalog from /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/data/parameters_data.yml
2026-01-14 11:21:21,206 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.wflow_base - wflow_base - INFO - Supported Wflow.jl version v1+
2026-01-14 11:21:21,206 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.config - config - INFO - Reading model config file from /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_subbasin/wflow_sbm.toml.
2026-01-14 11:21:21,207 - hydromt - log - INFO - HydroMT version: 1.3.0
2026-01-14 11:21:21,207 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.config - config - INFO - Reading model config file from /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_subbasin/wflow_sbm.toml.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,041 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.tables - tables - INFO - Reading model table files.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,042 - hydromt - log - INFO - HydroMT version: 1.3.0
2026-01-14 11:21:22,044 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - update: setup_config
2026-01-14 11:21:22,044 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_config.data={'time.starttime': datetime.datetime(2010, 2, 1, 0, 0), 'time.endtime': datetime.datetime(2010, 2, 10, 0, 0), 'time.timestepsecs': 86400, 'input.path_forcing': 'inmaps-chirps.nc'}
2026-01-14 11:21:22,044 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - update: setup_precip_forcing
2026-01-14 11:21:22,044 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_precip_forcing.precip_clim_fn=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,044 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_precip_forcing.chunksize=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,044 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_precip_forcing.precip_fn=chirps_global
2026-01-14 11:21:22,046 - hydromt.data_catalog.sources.data_source - data_source - INFO - Reading chirps_global RasterDataset data from /home/runner/.hydromt/artifact_data/latest/chirps_global.nc
2026-01-14 11:21:22,127 - hydromt.model.components.grid - grid - WARNING - Replacing grid map: precip
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - update: setup_temp_pet_forcing
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.pet_method=debruin
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.press_correction=True
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.temp_correction=True
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.wind_correction=True
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.wind_altitude=10
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.reproj_method=nearest_index
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.fillna_method=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.dem_forcing_fn=era5_orography
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.skip_pet=False
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.chunksize=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,128 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - setup_temp_pet_forcing.temp_pet_fn=era5
2026-01-14 11:21:22,130 - hydromt.data_catalog.sources.data_source - data_source - INFO - Reading era5 RasterDataset data from /home/runner/.hydromt/artifact_data/latest/era5.nc
2026-01-14 11:21:22,177 - hydromt.data_catalog.sources.data_source - data_source - INFO - Reading era5_orography RasterDataset data from /home/runner/.hydromt/artifact_data/latest/era5_orography.nc
2026-01-14 11:21:22,398 - hydromt.model.components.grid - grid - WARNING - Replacing grid map: pet
2026-01-14 11:21:22,403 - hydromt.model.components.grid - grid - WARNING - Replacing grid map: temp
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - update: forcing.write
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - forcing.write.filename=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - forcing.write.output_frequency=M
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - forcing.write.time_chunk=1
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - forcing.write.time_units=days since 1900-01-01T00:00:00
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - forcing.write.decimals=2
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - forcing.write.overwrite=False
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.forcing - forcing - INFO - Write forcing file
2026-01-14 11:21:22,404 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.forcing - forcing - WARNING - Start time 2010-02-01T00:00:00.000000 does not match the beginning of the data. Changing to start of the data: 2010-02-02T00:00:00.000000000.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,406 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.forcing - forcing - INFO - Writing several forcing with freq M
2026-01-14 11:21:22,412 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.forcing - forcing - INFO - Writing file /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/inmaps-chirps_20100202.nc
[########################################] | 100% Completed | 101.21 ms
2026-01-14 11:21:22,534 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - update: staticmaps.write
2026-01-14 11:21:22,534 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - staticmaps.write.filename=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,534 - hydromt.model.components.grid - grid - INFO - wflow_sbm.staticmaps: Writing grid data to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticmaps.nc.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,589 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - update: geoms.write
2026-01-14 11:21:22,589 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - geoms.write.folder=staticgeoms
2026-01-14 11:21:22,589 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - geoms.write.to_wgs84=False
2026-01-14 11:21:22,589 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - geoms.write.precision=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,610 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/region.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,612 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/basins.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,614 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/meta_basins_highres.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,625 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/gauges_grdc.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,627 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/outlets.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,629 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/glaciers.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,650 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/rivers.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,653 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/meta_reservoirs_no_control.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,655 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/reservoirs.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,657 - hydromt.model.components.geoms - geoms - INFO - wflow_sbm.geoms: Writing geoms to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/staticgeoms/meta_reservoirs_simple_control.geojson.
2026-01-14 11:21:22,661 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - update: config.write
2026-01-14 11:21:22,661 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - config.write.filename=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,661 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - config.write.config_root=None
2026-01-14 11:21:22,661 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.config - config - INFO - Writing model config to /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/wflow_sbm.toml.
The example above means the following: run hydromt with:
update wflow: i.e. update a wflow modelwflow_piave_subbasin: original model folder-o ./wflow_piave_forcing: output updated model folder-i wflow_update_forcing.yml: setup configuration file containing the components to update and their different options-d artifact_data: specify to use the artifact_data catalogv: give some extra verbosity (1 * v) to display feedback on screen. Now INFO messages are provided.
Model comparison#
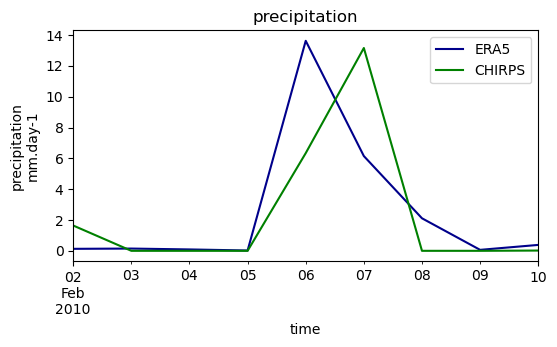
From the information above, you can see that the different forcing variables where updated. Compared to the original model, the temperature and potential evapotranspiration still come from the ERA5 data source but now the precipitation are using CHIRPS data.
Using the script from the plot example, we can compare the two precipitation datasets together (here basin average values).
[5]:
# Load both models with hydromt
from hydromt_wflow import WflowSbmModel
model0 = WflowSbmModel(root="wflow_piave_subbasin", mode="r")
model1 = WflowSbmModel(root="wflow_piave_forcing", mode="r")
2026-01-14 11:21:24,703 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - Initializing wflow_sbm model from hydromt_wflow (v1.0.1.dev0).
2026-01-14 11:21:24,704 - hydromt.data_catalog.data_catalog - data_catalog - INFO - Parsing data catalog from /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/data/parameters_data.yml
2026-01-14 11:21:24,734 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.wflow_base - wflow_base - INFO - Supported Wflow.jl version v1+
2026-01-14 11:21:24,735 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.config - config - INFO - Reading model config file from /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_subbasin/wflow_sbm.toml.
2026-01-14 11:21:24,736 - hydromt.model.model - model - INFO - Initializing wflow_sbm model from hydromt_wflow (v1.0.1.dev0).
2026-01-14 11:21:24,737 - hydromt.data_catalog.data_catalog - data_catalog - INFO - Parsing data catalog from /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/data/parameters_data.yml
2026-01-14 11:21:24,752 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.wflow_base - wflow_base - INFO - Supported Wflow.jl version v1+
2026-01-14 11:21:24,753 - hydromt.hydromt_wflow.components.config - config - INFO - Reading model config file from /home/runner/work/hydromt_wflow/hydromt_wflow/docs/_examples/wflow_piave_forcing/wflow_sbm.toml.
[6]:
# read wflow forcing
# NOTE: only very limited forcing data is available from the artifacts
ds_forcing0 = model0.forcing.data
ds_forcing0 = ds_forcing0.mean(dim=[ds_forcing0.raster.x_dim, ds_forcing0.raster.y_dim])
ds_forcing1 = model1.forcing.data
ds_forcing1 = ds_forcing1.mean(dim=[ds_forcing1.raster.x_dim, ds_forcing1.raster.y_dim])
[7]:
# plot precipitation
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 3))
df0 = ds_forcing0["precip"].squeeze().to_series()
df1 = ds_forcing1["precip"].squeeze().to_series()
# axes.bar(df1.index, df1.values, facecolor='green', label='CHIRPS')
# axes.bar(df0.index, df0.values, facecolor='darkblue', label='ERA5')
df0.plot.line(ax=axes, x="time", color="darkblue", label="ERA5")
df1.plot.line(ax=axes, x="time", color="green", label="CHIRPS")
axes.set_xlabel("time")
axes.legend()
axes.set_title("precipitation")
axes.set_ylabel("precipitation\nmm.day-1")
[7]:
Text(0, 0.5, 'precipitation\nmm.day-1')