Accessibility Analysis#
🚑 How quick can you reach essential services?#
Accessibility analysis in RA2CE answers practical questions like:
What is the shortest route from home to work?
Which is the quickest evacuation route to the hospital during an emergency?
How far is the closest school, shelter, or service from each neighborhood?
By analyzing origin–destination (OD) routes, RA2CE helps you explore connectivity under both normal and disrupted conditions.
Note
Accessibility analysis is built on the origin–destination (OD) framework. You provide one or more origins (start points) and destinations (end points), and RA2CE calculates the shortest or quickest route between them.
Preparing Origins and Destinations#
📍 Before running any OD analysis, you need to prepare two shapefiles: one for the origins (start points) and one for the destinations (end points).
These shapefiles must follow a specific data structure so that RA2CE can recognize them. For example, destinations can be grouped into categories such as hospitals, schools, or shelters.
Warning
If the shapefiles are not prepared correctly, the OD analysis will fail.
- 👉 For a full explanation of the required attributes and example files,
Case 1: Defined Origin–Destination Pairs#
In this mode, you provide a list of specific origin–destination pairs. RA2CE then computes the shortest or quickest route for each pair.
Typical use cases:
Checking travel time between specific towns or facilities
Studying accessibility between fixed points (e.g. home → workplace)
👉 See the detailed tutorial: Defined Origin–Destination Pairs
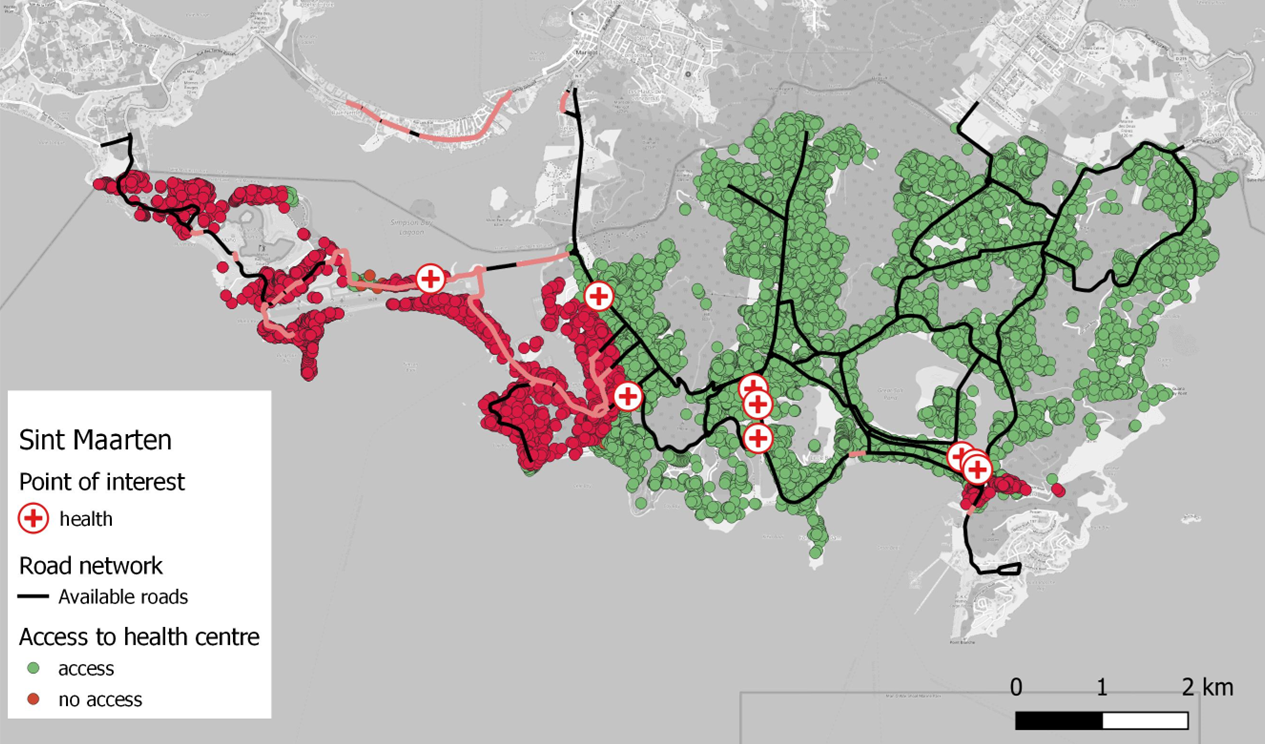
Case 2: Origins to Closest Destinations#
Instead of defining pairs, you can let RA2CE automatically find the closest destination for each origin.
Example: For every household (origin), RA2CE finds the nearest hospital, the nearest school, and the nearest shelter (destinations).
This is especially useful for:
Emergency planning (finding the nearest hospital or shelter)
Service accessibility (how close is the nearest school for each neighborhood?)
👉 See the detailed tutorial: Origins to Closest Destinations
When to Use Which?#
Use Defined Origin–Destination Pairs (Case 1) if you already know which specific locations you want to connect. Example: “From school X to hospital Y.”
Use Origins to Closest Destinations (Case 2) if you want to automatically find the nearest service from each origin. Example: “From every household/neighborhood to the closest hospital.”