Defined Origin–Destination Pairs Tutorial#
This tutorial demonstrates how to run a Defined Origin–Destination (OD) analysis with RA2CE. You explicitly provide origins and destinations, and RA2CE calculates shortest or quickest routes between them.
If you are not yet familiar with preparing origins and destinations shapefiles, see the Origins and Destinations Data Preparation tutorial.
Step 1: Import Libraries and Set Paths#
[ ]:
from pathlib import Path
from ra2ce.analysis.analysis_config_data.analysis_config_data import AnalysisSectionLosses, AnalysisConfigData
from ra2ce.analysis.analysis_config_data.enums.analysis_losses_enum import AnalysisLossesEnum
from ra2ce.analysis.analysis_config_data.enums.weighing_enum import WeighingEnum
from ra2ce.network.network_config_data.enums.road_type_enum import RoadTypeEnum
from ra2ce.network.network_config_data.enums.network_type_enum import NetworkTypeEnum
from ra2ce.network.network_config_data.enums.source_enum import SourceEnum
from ra2ce.network.network_config_data.network_config_data import (
NetworkSection, NetworkConfigData, OriginsDestinationsSection
)
from ra2ce.ra2ce_handler import Ra2ceHandler
# Specify the path to your RA2CE project folder and input data
root_dir = Path("data", "pairs_origins_destinations")
network_path = root_dir.joinpath('static', 'network')
Step 2: Define Network with Origins & Destinations#
Define the network configuration, in this case downloaded from OSM and clipped to a region polygon. Only specific road types are included.
[ ]:
network_section = NetworkSection(
source=SourceEnum.OSM_DOWNLOAD,
polygon=network_path.joinpath("region_polygon.geojson"),
network_type=NetworkTypeEnum.DRIVE,
road_types=[
RoadTypeEnum.MOTORWAY,
RoadTypeEnum.MOTORWAY_LINK,
RoadTypeEnum.PRIMARY,
RoadTypeEnum.PRIMARY_LINK,
RoadTypeEnum.SECONDARY,
RoadTypeEnum.SECONDARY_LINK,
RoadTypeEnum.TERTIARY,
RoadTypeEnum.TERTIARY_LINK,
RoadTypeEnum.RESIDENTIAL,
],
save_gpkg=True,
reuse_network_output=True,
)
Define origins and destinations shapefiles using OriginsDestinationsSection. Specify the shortcut names and attributes in the shapefiles.
[ ]:
origin_destination_section = OriginsDestinationsSection(
origins=network_path.joinpath("origins.shp"),
destinations=network_path.joinpath("destinations.shp"),
origin_count="POPULATION",
)
[ ]:
network_config_data = NetworkConfigData(
root_path=root_dir,
static_path=root_dir.joinpath('static'),
network=network_section,
origins_destinations=origin_destination_section,
)
Step 3: Define the Analysis#
Specify the analysis type as AnalysisLossesEnum.OPTIMAL_ROUTE_ORIGIN_DESTINATION, which calculates optimal routes for the OD pairs.
[ ]:
analyse_section = AnalysisSectionLosses(
name="origin_destination_without_hazard",
analysis=AnalysisLossesEnum.OPTIMAL_ROUTE_ORIGIN_DESTINATION,
weighing=WeighingEnum.LENGTH,
calculate_route_without_disruption=True,
save_csv=True,
save_gpkg=True,
)
analysis_config_data = AnalysisConfigData(
output_path=root_dir.joinpath("output"),
static_path=root_dir.joinpath('static'),
analyses=[analyse_section],
)
Step 4: Run the Analysis#
Use Ra2ceHandler to configure and run the analysis.
[ ]:
handler = Ra2ceHandler.from_config(
network=network_config_data,
analysis=analysis_config_data
)
handler.configure()
handler.run_analysis()
Step 5: Inspect Results#
Results are stored in the output folder and include both CSV and GeoPackage (GPKG) files. You can open the GPKG in GIS software or load it in Python using GeoPandas.
[ ]:
import geopandas as gpd
results_gpkg = root_dir.joinpath(
"output",
"optimal_route_origin_destination",
"origin_destination_without_hazard.gpkg"
)
gdf = gpd.read_file(results_gpkg)
gdf.head()
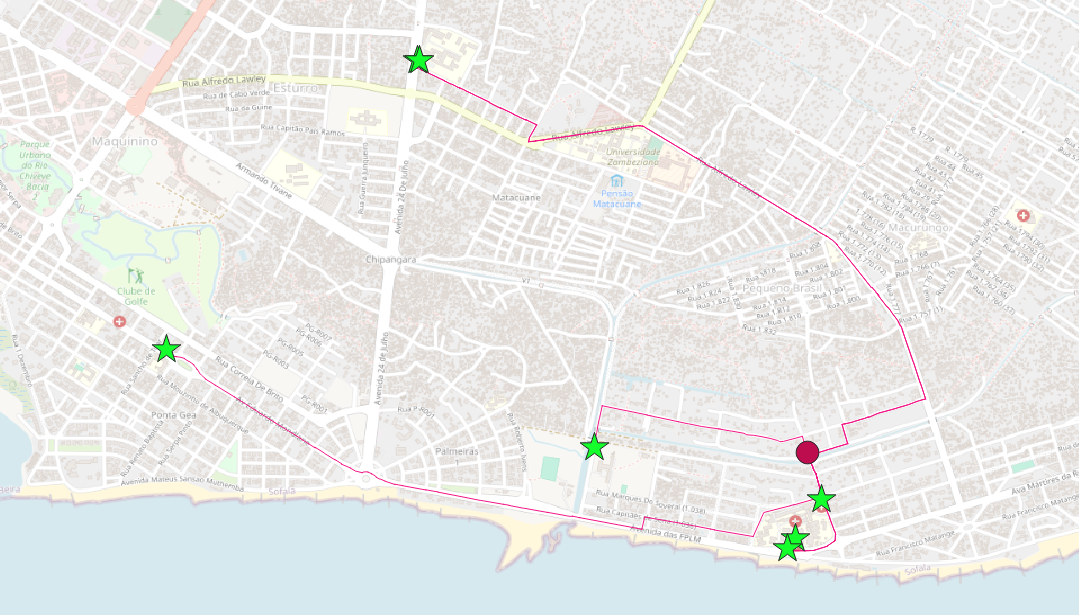 All shortest routes from a chosen origin (red circle) to all possible destinations (green stars).
All shortest routes from a chosen origin (red circle) to all possible destinations (green stars).