Explaining the Wflow - DELWAQ coupling#
Water quality and emission, fate and transport of pollutants through the landscape is very much linked to the water movements. In most cases, pollutants are emitted on land and either leach into the soil or are picked up by water during rain events and transported towards and into the rivers. In order to model water quality is it therefore essential to first understand and assess the hydrology of the catchment / region of interests.
A full hydrology - water quality modelling suite is in general separated in three parts:
the hydrological model, wflow_sbm, that predicts water movements through the catchments.
an emission model, D-Emissions (also referred to as EM in hydroMT), that predicts the quantity (fluxes) of substances being released from sources of pollutants to the surface waters (mass/time).
a fate and transport model, D-Water Quality (also referred to as WQ in hydroMT), that predicts the fate and transport of substances in the surface waters (concentrations in mass / volume).
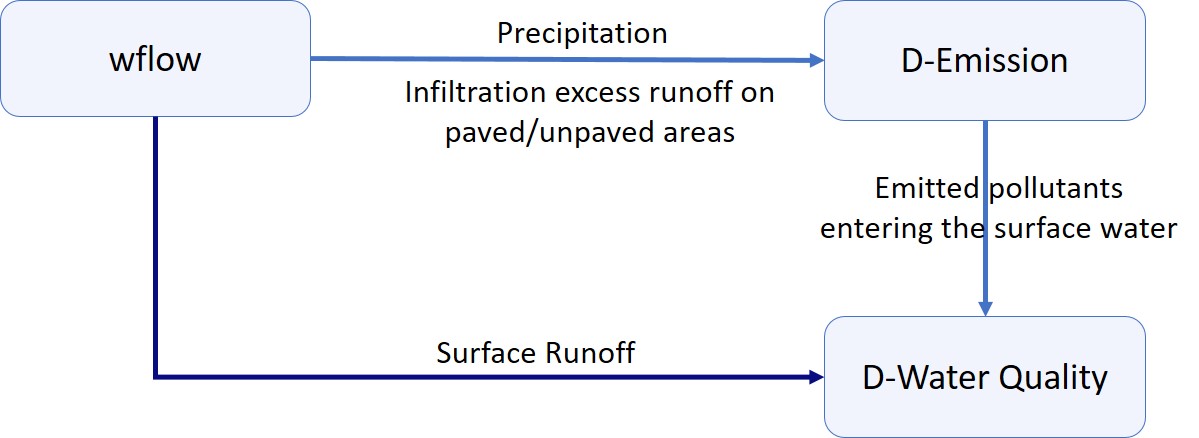
For the purpose of modelling catchment water quality, the wflow_sbm model has been linked to EM and WQ (both based on DELWAQ, Deltares water quality software) using a “coupling” function integrated in the HydroMT-delwaq plugin.
The wflow-DELWAQ coupling function in HydroMT:
translates wflow schematization to DELWAQ schematization;
prepares static inputs needed for water quality modelling (emission sources, locators…);
prepares dynamic inputs needed for water quality modelling (different water fluxes and volumes);
supports the modelling of different types of pollutants.
A full hydrology - water quality modelling suite is setup and run using the following steps:
Hydrological modelling with wflow
Run wflow in order to prepare the hydrological fluxes required by EM and WQ.
Emissions modelling with D-Emissions
Setup the EM model from wflow and emission data using hydroMT
Edit the EM run info and run D-Emission (EM-Plugin)
Fate and transport modelling with D-Water Quality
Setup the WQ model from wflow and emission data using hydroMT
Link EM results to WQ
Edit the WQ run info and run D-Water Quality (WQ-Plugin)
Hydrological forcing from Wflow#
In order to determine how and where substances are emitted and how they move through the landscape via the surface water, water quality modelling requires certain hydrological information.
For an EM type of model (emission of substances in the surface waters), the required information is:
precipitation;
the amount of the precipitation that infiltrates into the soil from unpaved areas
the amount of the precipitation that goes directly to surface runoff from paved areas
the amount of the precipitation that goes directly to surface runoff from unpaved areas
exfiltration from the unsaturated and saturated soil to the surface waters
overland flow and subsurface flow
moisture in the root zone
For a WQ type of model (fate and transport of substances in the surface waters), the required information is:
River discharge
River volumes
Water entering the surface waters (from overland flow and subsurface flow).
Wflow separates and routes water for three different components, the surface waters on the land, the river surface water and the water in the soil. D-Emissions handles processes occurring on the land and subsurface, while D-Water Quality handles processes occurring in the river surface water.
In order to prepare hydrological fluxes for DELWAQ from Wflow, Wflow should be run and the required fluxes saved (same order as above):
atmosphere_water__precipitation_volume_flux (precipitation input)
land_surface__evapotranspiration_volume_flux (infiltration in the soil)
non_compacted_soil_surface_water__excess_volume_flux (infiltration excess runoff on paved areas)
compacted_soil_surface_water__excess_volume_flux (infiltration excess runoff on unpaved areas)
soil_surface_water_unsaturated_zone__exfiltration_volume_flux (exfiltration from unsaturated zone)
soil_surface_water_saturated_zone__exfiltration_volume_flux (exfiltration from saturated zone)
land_surface_water__volume_flow_rate (overland flow)
subsurface_water__volume_flow_rate (subsurface flow)
soil_water_root_zone__volume_percentage (moisture in the root zone)
river_water__volume_flow_rate (runoff in the river kinematic wave)
river_water__volume (kinematic wave volume in the river and on the land)
land_surface_water__to_river_volume_flow_rate and subsurface_water__to_river_volume_flow_rate (inflows to the river from overland flow and subsurface flow).