User guide#
HydroMT is a Python package that aims to facilitate the process of building models and analyzing model results by automating the process to go from raw data to model data. It is an interface between user, data and hydro models.
HydroMT is organized in the following way:
Input Data
HydroMT is data-agnostic through the Data Adapter, which reads a wide range of data formats and unifies the input data . Datasets are listed and passed to HydroMT in a user defined data catalog yaml file. HydroMT also provides several pre-defined data catalogs with mostly global datasets that can be used as is, although not all datasets in these catalogs are openly accessible. Currently, four different types of input data are supported and represented by a specific Python data object by HydroMT: gridded datasets such as DEMs or gridded spatially distributed rainfall datasets (represented by RasterDataset objects); tables for e.g. reclassification to convert land classes use into roughness values (represented by DataFrame objects); vector datasets such as administrative units or river center lines (represented by GeoDataFrame objects); and time series with associated geolocations such as observations of discharge (represented by GeoDataset objects).
Models
HydroMT defines any model through the model-agnostic Model API based on several components: maps, geometries, forcing, results, states and the model simulation configuration. For different types of general model classes additional model components (e.g. response units for lumped or semi-distributed models). Each component is represented with a specific Python data object to provide a common interface to different model software. Models can be built from scratch, and existing models can be updated based on a pipeline of methods defined in a model configuration ini file. While HydroMT provides several general model classes which can readily be used, it can also be tailored to specific model software through a plugin infrastructure. These plugins have the same interface, but with model-specific file readers and writers and workflows.
Methods and workflow
Methods and workflows are the engine of HydroMT, indicated by the gear wheels in the figure below. Methods provide the low-level functionality such as GIS rasterization, reprojection or zonal statistics. Workflows combine several methods to transform data to a model layer. Examples of workflows include the delineation of hydrological basins (watersheds), and conversion of landuse-landcover data to model parameter maps. Workflows are implemented for the data types mentioned above to allow reusing common workflows between HydroMT plugins for different model software.
A user can interact with HydroMT through the following interfaces:
Command Line Interface (CLI)
The CLI is a high-level interface to HydroMT. It is used to run HydroMT methods such as build, update or clip.
Python Interface
While most common functionalities can be called through the CLI, the Python interface offers more flexibility for advanced users. It allows you to e.g. interact directly with a model component Model API and apply the many methods and workflows available. Please find all available functions API reference
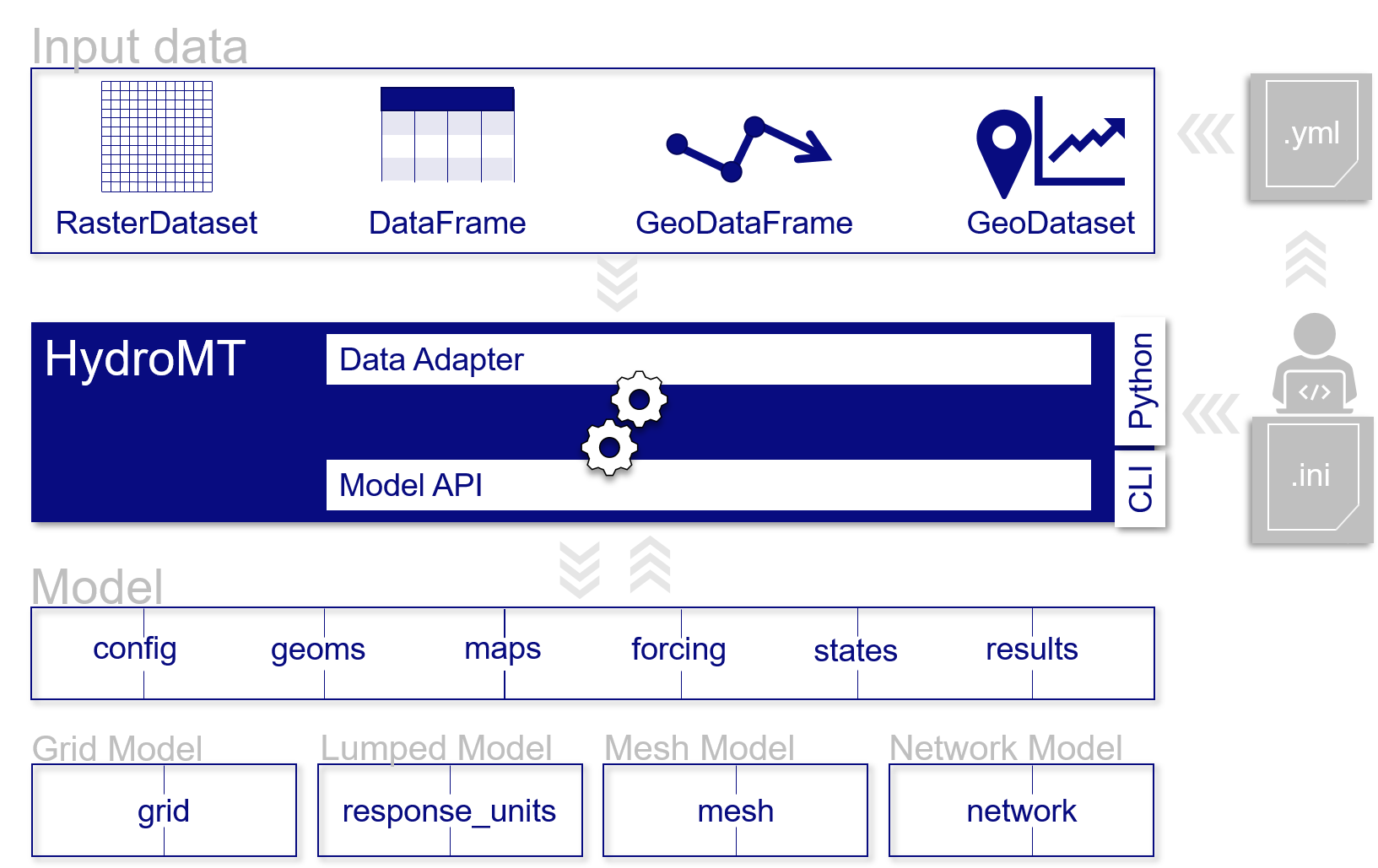
Schematic of HydroMT architecture#
Terminology#
HydroMT and this documentation use a specific terminology to describe specific objects or processes.
Term |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Command Line Interface (CLI) |
high-level interface to HydroMT build, update and clip methods. |
Configuration (HydroMT) |
(.ini) file describing the complete pipeline with all methods and their arguments to build or update a model. |
Data catalog |
A set of data sources available for HydroMT. It is build up from yaml files containing one or more data sources with information about how to read and optionally preprocess the data and contains meta-data about the data source. |
Data source |
Input data to be processed by HydroMT. Data sources are listed in yaml files. |
Model |
A set of files describing the schematization, forcing, states, simulation configuration and results for any supported model kernel and model classes. The final set of files is dependent on the model type (grid, lumped or mesh model for examples) or the model plugin. |
Model class |
A model instance can be instantiated from different model schematization concepts. Generalized model classes currently supported within HydroMT are Grid Model (distributed models), Lumped Model (semi-distributed), Mesh Model (unstructured) and in the future Network Model (relational model). Specific model classes for specific softwares have been implemented as plugins, see Model plugin. |
Model attributes |
Direct properties of a model, such as the model root. They can be called when using HydroMT from python. |
Model component |
A model is described by HydroMT with the following components: maps, geoms (vector data), forcing, results, states, config, grid (for a grid model), response_units (for a lumped model), mesh (for a mesh model). |
Model plugin |
Model software for which HydroMT can build and update models and analyze its simulation results. For example Wflow, SFINCS etc. |
Model kernel |
The model software to execute a model simulation. This is not part of any HydroMT plugin. |
Region |
Argument of the build and clip CLI methods that specifies the region of interest where the model should be prepared / which spatial subregion should be clipped. |